State Opening Of Parliament on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The State Opening of Parliament is a ceremonial event which formally marks the beginning of a session of the
The State Opening of Parliament is a ceremonial event which formally marks the beginning of a session of the
 The State Opening of Parliament is a ceremony filled with historical ritual and symbolic significance for the governance of the United Kingdom. In one place are assembled the members of all three branches of government, of which the Monarch is the authority and nominal head in each part: the
The State Opening of Parliament is a ceremony filled with historical ritual and symbolic significance for the governance of the United Kingdom. In one place are assembled the members of all three branches of government, of which the Monarch is the authority and nominal head in each part: the


 The ceremonial surrounding the opening of parliament can be broken down into several parts (the following descriptions refer to the full ceremonial of the event; for occasions when, for various reasons, reduced ceremonial has been used, see below):
The ceremonial surrounding the opening of parliament can be broken down into several parts (the following descriptions refer to the full ceremonial of the event; for occasions when, for various reasons, reduced ceremonial has been used, see below):
 Before the arrival of the sovereign, the
Before the arrival of the sovereign, the
 The monarch travels to the Palace of Westminster from Buckingham Palace in a state coach (since 2014, the
The monarch travels to the Palace of Westminster from Buckingham Palace in a state coach (since 2014, the
 Motioned by the monarch, the Lord Great Chamberlain raises his white staff of office to signal the official known as Black Rod to summon the House of Commons. Black Rod turns and, under the escort of the Door-keeper of the House of Lords, proceeds to the Members' Lobby of the
Motioned by the monarch, the Lord Great Chamberlain raises his white staff of office to signal the official known as Black Rod to summon the House of Commons. Black Rod turns and, under the escort of the Door-keeper of the House of Lords, proceeds to the Members' Lobby of the  This ritual is strongly associated with the occasion when (in 1642) King
This ritual is strongly associated with the occasion when (in 1642) King
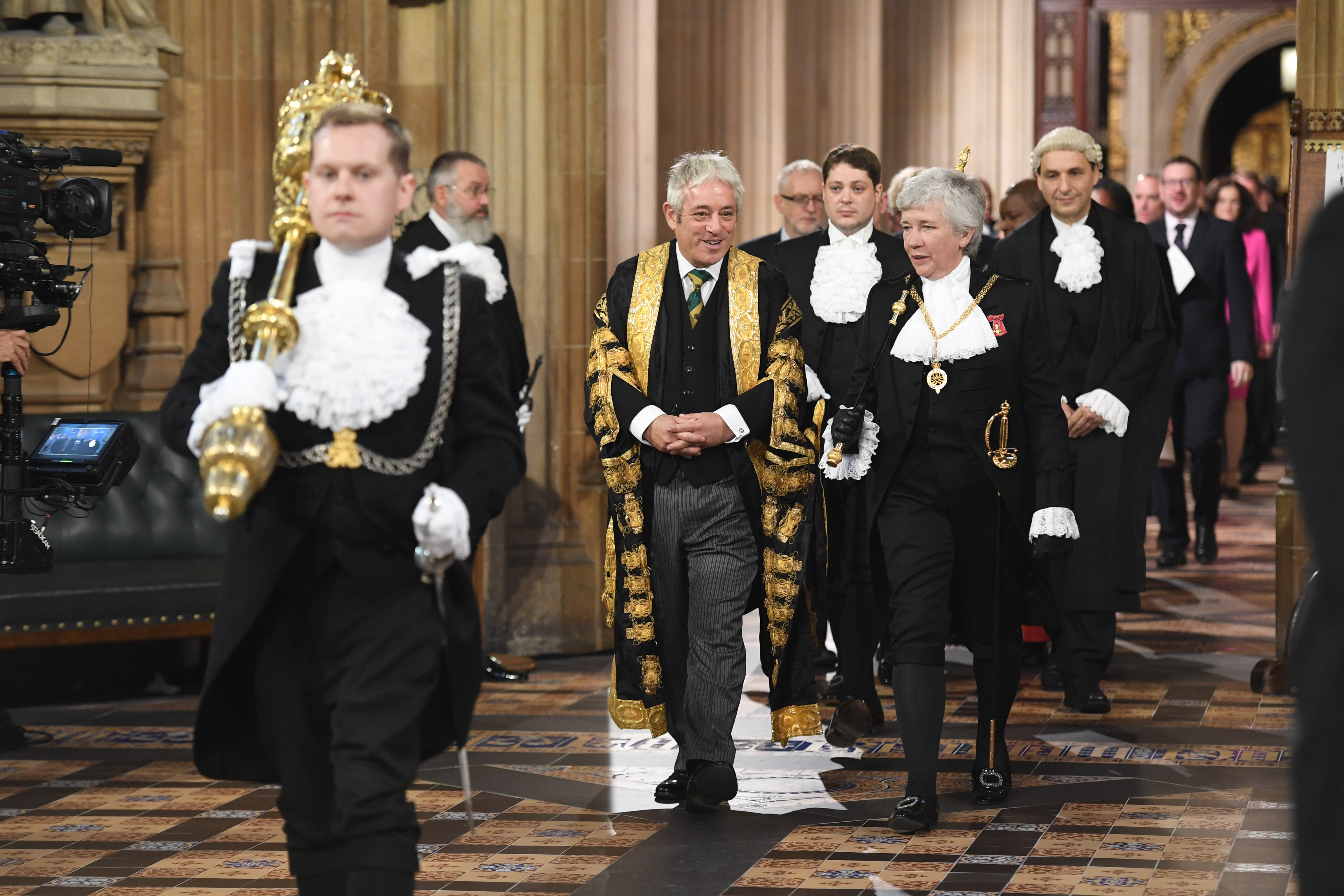 The Speaker proceeds to attend the summons at once. The Serjeant-at-Arms picks up the ceremonial mace and, with the Speaker and Black Rod, leads the Members of the House of Commons as they walk, in pairs, towards the House of Lords. By custom, the members saunter, with much discussion and joking, rather than formally process. The
The Speaker proceeds to attend the summons at once. The Serjeant-at-Arms picks up the ceremonial mace and, with the Speaker and Black Rod, leads the Members of the House of Commons as they walk, in pairs, towards the House of Lords. By custom, the members saunter, with much discussion and joking, rather than formally process. The
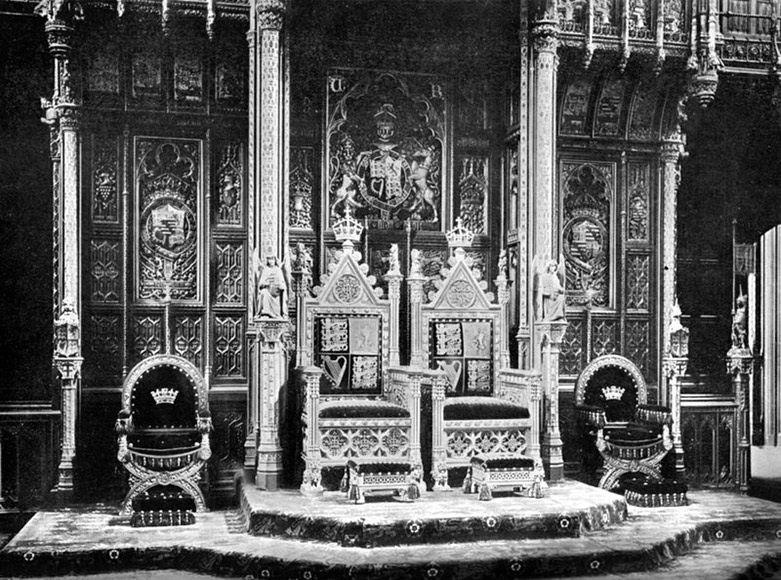
 The monarch reads a prepared speech, known as the "
The monarch reads a prepared speech, known as the "

 Following the speech, the monarch and his or her retinue leave the chamber. The monarch bows to both sides of the House of Peers and then leaves the chamber, in the reverse order of the usual procession, before the Commons bow again and return to their Chamber.
Following the speech, the monarch and his or her retinue leave the chamber. The monarch bows to both sides of the House of Peers and then leaves the chamber, in the reverse order of the usual procession, before the Commons bow again and return to their Chamber.
 The Wriothesley Garter Book, a 1523 illustration by
The Wriothesley Garter Book, a 1523 illustration by
/ref> The
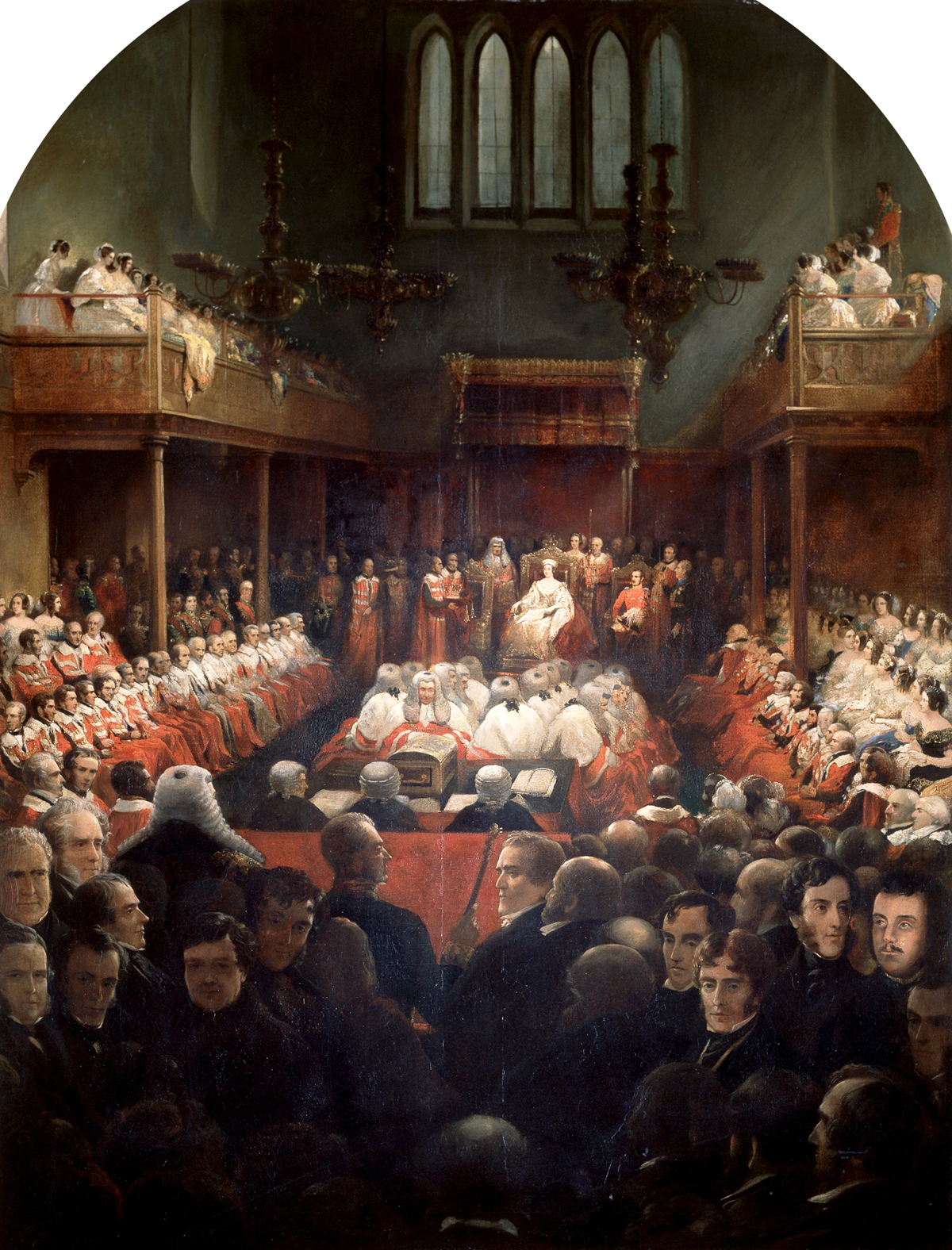 Since that time the ceremonial has evolved, but not dramatically. In 1679 neither the procession nor the Abbey service took place, due to fears of a Popish Plot; although the procession was subsequently restored, the service in the Abbey was not. The monarch's role in the proceedings changed over time: early on, the monarch would say some introductory words, before calling upon the Lord Chancellor (or Lord Keeper) to address the assembly. James I, however, was accustomed to speak at greater length himself, and sometimes dispensed with the Chancellor's services as spokesman. This varying pattern continued in subsequent reigns (and during the Commonwealth, when Cromwell gave the speech), but from 1679 onwards it became the norm for the monarch alone to speak. Since then, the monarch (if present) has almost invariably given the speech, with the exception of George I (whose command of English was poor) and Victoria (after the death of Prince Albert). A dramatic change was occasioned by the destruction of the old Palace of Westminster by fire in 1834; however, the new palace was designed with the ceremony of the State Opening very much in mind, and the modern ceremony dates from its opening in 1852. The entire State Opening of Parliament was filmed and televised for the first time in 1958.
In 1998, adjustments were made to the ceremonial inside Parliament to shorten the proceedings. The
Since that time the ceremonial has evolved, but not dramatically. In 1679 neither the procession nor the Abbey service took place, due to fears of a Popish Plot; although the procession was subsequently restored, the service in the Abbey was not. The monarch's role in the proceedings changed over time: early on, the monarch would say some introductory words, before calling upon the Lord Chancellor (or Lord Keeper) to address the assembly. James I, however, was accustomed to speak at greater length himself, and sometimes dispensed with the Chancellor's services as spokesman. This varying pattern continued in subsequent reigns (and during the Commonwealth, when Cromwell gave the speech), but from 1679 onwards it became the norm for the monarch alone to speak. Since then, the monarch (if present) has almost invariably given the speech, with the exception of George I (whose command of English was poor) and Victoria (after the death of Prince Albert). A dramatic change was occasioned by the destruction of the old Palace of Westminster by fire in 1834; however, the new palace was designed with the ceremony of the State Opening very much in mind, and the modern ceremony dates from its opening in 1852. The entire State Opening of Parliament was filmed and televised for the first time in 1958.
In 1998, adjustments were made to the ceremonial inside Parliament to shorten the proceedings. The
 Similar ceremonies are held in other
Similar ceremonies are held in other  In the
In the
Videos of every State Opening since 1988
at
House of Lords FAQ: State Opening
at UK Parliament website
Parliamentary occasions: State Opening
at UK Parliament website
at
Photos of the 2015 ceremony
at
Newsreel of the 1958 ceremony
(the first time the ceremony was filmed)
Newsreel of the 1960 ceremony
(filmed for the first time in colour)
Newsreel of the 1966 ceremony
(the first time cameras were allowed in the House of Commons)
Newsreel of the 1970 ceremony
Newsreel of the November 1974 ceremony
(the second State Opening of that year) {{DEFAULTSORT:State Opening of Parliament Speeches by heads of state Parliament of the United Kingdom Opening ceremonies Ceremonies in the United Kingdom
 The State Opening of Parliament is a ceremonial event which formally marks the beginning of a session of the
The State Opening of Parliament is a ceremonial event which formally marks the beginning of a session of the Parliament of the United Kingdom
The Parliament of the United Kingdom is the supreme legislative body of the United Kingdom, the Crown Dependencies and the British Overseas Territories. It meets at the Palace of Westminster, London. It alone possesses legislative suprema ...
. It includes a speech from the throne
A speech from the throne, or throne speech, is an event in certain monarchies in which the reigning sovereign, or a representative thereof, reads a prepared speech to members of the nation's legislature when a session is opened, outlining th ...
known as the King's (or Queen's) Speech. The event takes place in the House of Lords
The House of Lords, also known as the House of Peers, is the Bicameralism, upper house of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. Membership is by Life peer, appointment, Hereditary peer, heredity or Lords Spiritual, official function. Like the ...
chamber on the first day of a new session, which is usually in May or June, and traditionally in November, but can occur at any time of year depending on the timing of General Elections and parliamentary session start dates. It takes place in front of both Houses of Parliament. The monarch, wearing the Imperial State Crown
The Imperial State Crown is one of the Crown Jewels of the United Kingdom and symbolises the sovereignty of the monarch.
It has existed in various forms since the 15th century. The current version was made in 1937 and is worn by the monarc ...
, reads a speech that has been prepared by his or her government outlining its plans for that parliamentary year.
The most recent ceremony was held on 10 May 2022.
Queen Elizabeth II
Elizabeth II (Elizabeth Alexandra Mary; 21 April 1926 – 8 September 2022) was Queen of the United Kingdom and other Commonwealth realms from 6 February 1952 until her death in 2022. She was queen regnant of 32 sovereign states during ...
opened every session of Parliament during her reign, except in 1959, 1963, and 2022. In 1959 and 1963, she was pregnant with Prince Andrew
Prince Andrew, Duke of York, (Andrew Albert Christian Edward; born 19 February 1960) is a member of the British royal family. He is the younger brother of King Charles III and the third child and second son of Queen Elizabeth II and Prince ...
and Prince Edward respectively and those two sessions were opened by Lords Commissioners
The Lords Commissioners are privy counsellors appointed by the monarch of the United Kingdom to exercise, on his or her behalf, certain functions relating to Parliament which would otherwise require the monarch's attendance at the Palace of Wes ...
, headed by the Archbishop of Canterbury
The archbishop of Canterbury is the senior bishop and a principal leader of the Church of England, the ceremonial head of the worldwide Anglican Communion and the diocesan bishop of the Diocese of Canterbury. The current archbishop is Justi ...
(Geoffrey Fisher
Geoffrey Francis Fisher, Baron Fisher of Lambeth, (5 May 1887 – 15 September 1972) was an English Anglican priest, and 99th Archbishop of Canterbury, serving from 1945 to 1961.
From a long line of parish priests, Fisher was educated at Marlb ...
in 1959 and Michael Ramsey
Arthur Michael Ramsey, Baron Ramsey of Canterbury, (14 November 1904 – 23 April 1988) was an English Anglican bishop and life peer. He served as the 100th Archbishop of Canterbury. He was appointed on 31 May 1961 and held the office until 1 ...
in 1963), empowered by the Queen. The Lord Chancellor
The lord chancellor, formally the lord high chancellor of Great Britain, is the highest-ranking traditional minister among the Great Officers of State in Scotland and England in the United Kingdom, nominally outranking the prime minister. The ...
(Viscount Kilmuir
A viscount ( , for male) or viscountess (, for female) is a title used in certain European countries for a noble of varying status.
In many countries a viscount, and its historical equivalents, was a non-hereditary, administrative or judicial ...
in 1959 and Lord Dilhorne in 1963) read the Queen's Speech on those occasions. The Queen also missed the 2022 State Opening on the advice of her doctors. That session was opened by her son Charles, Prince of Wales
Charles III (Charles Philip Arthur George; born 14 November 1948) is King of the United Kingdom and the 14 other Commonwealth realms. He was the longest-serving heir apparent and Prince of Wales and, at age 73, became the oldest person to a ...
and her grandson Prince William, Duke of Cambridge who, in their capacity as Counsellors of State
Counsellors of State are senior members of the British royal family to whom the monarch can delegate and revoke royal functions through letters patent under the Great Seal, to prevent delay or difficulty in the dispatch of public business in t ...
, were empowered to do so by Letters Patent issued by the Queen for the occasion, the Prince of Wales reading the Queen's Speech (from the consort's throne) on behalf of his mother.
Significance
Crown-in-Parliament
The King-in-Parliament (or, during the reign of a female monarch, Queen-in-Parliament), sometimes referred neutrally as the Crown-in-Parliament, is a technical term of constitutional law in the Commonwealth realms that refers to the Crown in i ...
(the Monarch, together with the House of Commons and the House of Lords) constitutes the legislature; the King- (or Queen-) in-Council, His (or Her) Majesty's Ministers (who are members of one or other House, and members of the Monarch's Privy Council
A privy council is a body that advises the head of state of a state, typically, but not always, in the context of a monarchic government. The word "privy" means "private" or "secret"; thus, a privy council was originally a committee of the mon ...
) constitute the executive; the King- (or Queen-) on-the-Bench, consisting of His or Her Majesty's Judges, although not members of either House, are summoned to attend and represent the judiciary
The judiciary (also known as the judicial system, judicature, judicial branch, judiciative branch, and court or judiciary system) is the system of courts that adjudicates legal disputes/disagreements and interprets, defends, and applies the law ...
. Therefore, the State Opening demonstrates the governance of the United Kingdom but also the separation of powers
Separation of powers refers to the division of a state's government into branches, each with separate, independent powers and responsibilities, so that the powers of one branch are not in conflict with those of the other branches. The typic ...
. The importance of international relations is also represented through the presence in the Chamber of the ''corps diplomatique
The diplomatic corps (french: corps diplomatique) is the collective body of foreign diplomats accredited to a particular country or body.
The diplomatic corps may, in certain contexts, refer to the collection of accredited heads of mission ( a ...
''.
Sequence of events


 The ceremonial surrounding the opening of parliament can be broken down into several parts (the following descriptions refer to the full ceremonial of the event; for occasions when, for various reasons, reduced ceremonial has been used, see below):
The ceremonial surrounding the opening of parliament can be broken down into several parts (the following descriptions refer to the full ceremonial of the event; for occasions when, for various reasons, reduced ceremonial has been used, see below):
Searching of the cellars
First, the cellars of the Palace of Westminster are searched by theYeomen of the Guard
The King's Body Guard of the Yeomen of the Guard is a bodyguard of the British monarch. The oldest British military corps still in existence, it was created by King Henry VII in 1485 after the Battle of Bosworth Field.
History
The king ...
in order to prevent a modern-day Gunpowder Plot
The Gunpowder Plot of 1605, in earlier centuries often called the Gunpowder Treason Plot or the Jesuit Treason, was a failed assassination attempt against King James I by a group of provincial English Catholics led by Robert Catesby who sough ...
. The Plot of 1605 involved a failed attempt by a group of provincial English Catholics led by Robert Catesby
Robert Catesby (c. 1572 – 8 November 1605) was the leader of a group of English Catholics who planned the failed Gunpowder Plot of 1605.
Born in Warwickshire, Catesby was educated in Oxford. His family were prominent recusant Catholics, and ...
to blow up the Houses of Parliament and kill the Protestant King James I
James VI and I (James Charles Stuart; 19 June 1566 – 27 March 1625) was King of Scotland as James VI from 24 July 1567 and King of England and Ireland as James I from the union of the Scottish and English crowns on 24 March 1603 until hi ...
and aristocracy. Since that year, the cellars have been searched, now largely, but not only, for ceremonial purposes. This is supervised by the Lord Great Chamberlain, and the Yeomen are paid for their services with a small glass of port wine
Port wine (also known as vinho do Porto, , or simply port) is a Portuguese fortified wine produced in the Douro Valley of northern Portugal. It is typically a sweet red wine, often served with dessert, although it also comes in dry, semi- ...
.
Assembly of Peers and Commons
Peers and peeresses assemble in the House of Lords. The Lords Spiritual and theLords Temporal
The Lords Temporal are secular members of the House of Lords, the upper house of the British Parliament. These can be either life peers or hereditary peers, although the hereditary right to sit in the House of Lords was abolished for all but n ...
wear their Parliament robes for the occasion. They are joined by senior representatives of the judiciary, who sit on woolsack
The Woolsack is the seat of the Lord Speaker in the House of Lords, the Upper House of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. Before 2006, it was the seat of the Lord Chancellor.
History
In the 14th century King Edward III (1327–1377) said th ...
s in the centre of the Chamber, and members of the diplomatic corps, who are seated behind the Bishops. The Commons assemble in their own chamber, wearing ordinary day dress, and begin the day, as any other, with prayers. Beforehand the Speaker's Procession takes place in the usual way: preceded by a doorkeeper, the Serjeant at Arms
A serjeant-at-arms, or sergeant-at-arms, is an officer appointed by a deliberative body, usually a legislature, to keep order during its meetings. The word "serjeant" is derived from the Latin ''serviens'', which means "servant". Historically, s ...
, leads the Speaker of the House of Commons Speaker of the House of Commons is a political leadership position found in countries that have a House of Commons, where the membership of the body elects a speaker to lead its proceedings.
Systems that have such a position include:
* Speaker of ...
from his official residence to the Commons Chamber, followed by his trainbearer, chaplain and secretary. In the Central Lobby, a police inspector
Inspector, also police inspector or inspector of police, is a police rank. The rank or position varies in seniority depending on the organization that uses it.
Australia
In Australian police forces, the rank of inspector is generally the ne ...
makes the traditional cry of "Hats off, strangers", instructing those assembled to remove their hats in deference to the highest-ranking commoner in the realm.
Delivery of parliamentary hostage
On the morning of the State Opening, theTreasurer
A treasurer is the person responsible for running the treasury of an organization. The significant core functions of a corporate treasurer include cash and liquidity management, risk management, and corporate finance.
Government
The treasury ...
, Comptroller and Vice-Chamberlain of the Household (all of whom are government whips) assemble with other senior members of the Royal Household at Buckingham Palace, carrying their ceremonial white staves of office. The Treasurer and Comptroller, along with other senior members of the Royal Household, accompany the monarch in the carriage procession; but the Lord Chamberlain
The Lord Chamberlain of the Household is the most senior officer of the Royal Household of the United Kingdom, supervising the departments which support and provide advice to the Sovereign of the United Kingdom while also acting as the main c ...
does not join them. Instead, on behalf of the monarch, he remains at Buckingham Palace keeping one MP (the Vice-Chamberlain) "hostage" for the duration of the state opening, by tradition as a surety for the safe return of the monarch. The hostage MP is well entertained until the successful conclusion of the ceremony, when they are released upon the safe return of the monarch. The Vice-Chamberlain's imprisonment is now purely ceremonial, though they do remain under guard; originally, it guaranteed the safety of the Sovereign as they entered a possibly hostile Parliament. The tradition is said to stem from the time of Charles I Charles I may refer to:
Kings and emperors
* Charlemagne (742–814), numbered Charles I in the lists of Holy Roman Emperors and French kings
* Charles I of Anjou (1226–1285), also king of Albania, Jerusalem, Naples and Sicily
* Charles I of ...
, who had a contentious relationship with Parliament and was eventually beheaded in 1649 during the Civil War
A civil war or intrastate war is a war between organized groups within the same state (or country).
The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies ...
between the monarchy and Parliament (a copy of Charles I's death warrant is displayed in the robing room used by the monarch as a ceremonial reminder of what can happen to a monarch who attempts to interfere with Parliament); however it has been suggested that the custom in its present form is of much more recent origin (mention of hostage-taking only dating back to the 1960s or 70s). In 1845, by contrast, the Lord Chamberlain's routine absence from the State Opening was said to be due to 'the department over which his lordship presides not being acknowledged in His Majesty's Palace at Westminster' (where the Lord Great Chamberlain instead has the equivalent authority).
Hostage MPs in recent years (all of whom were serving as Vice-Chamberlain of the Household at the time) have included:
* 2014: Desmond Swayne
Sir Desmond Angus Swayne (born 20 August 1956) is a British Conservative politician serving as the Member of Parliament for the constituency of New Forest West since 1997.
Before going into politics, Swayne was a teacher, and then a manager a ...
* 2015–16: Kris Hopkins
Kristan Frederick Hopkins (born 8 June 1963) is a British Conservative Party politician, who was formerly the Member of Parliament for Keighley in West Yorkshire. Elected in 2010, he served as Vice-Chamberlain of the Household, a government wh ...
* 2017: Chris Heaton-Harris
* 2019: Stuart Andrew
Stuart James Andrew (born 25 November 1971) is a Welsh politician serving as Parliamentary Under-Secretary of State for Sport, Tourism, Heritage and Civil Society since September 2022 and Parliamentary Under-Secretary of State for Equalities s ...
* 2021
File:2021 collage V2.png, From top left, clockwise: the James Webb Space Telescope was launched in 2021; Protesters in Yangon, Myanmar following the 2021 Myanmar coup d'état, coup d'état; A civil demonstration against the October–November 2021 ...
: Marcus Jones
* 2022
File:2022 collage V1.png, Clockwise, from top left: Road junction at Yamato-Saidaiji Station several hours after the assassination of Shinzo Abe; 2022 Sri Lankan protests, Anti-government protest in Sri Lanka in front of the Presidential Secretari ...
: James Morris
Arrival of royal regalia
 Before the arrival of the sovereign, the
Before the arrival of the sovereign, the Imperial State Crown
The Imperial State Crown is one of the Crown Jewels of the United Kingdom and symbolises the sovereignty of the monarch.
It has existed in various forms since the 15th century. The current version was made in 1937 and is worn by the monarc ...
is brought to the Palace of Westminster, together with the Great Sword of State and the Cap of Maintenance
Typical of British heraldry, a cap of maintenance, known in heraldic language as a ''chapeau gules turned up ermine'', is a ceremonial cap of crimson velvet lined with ermine, which is worn or carried by certain persons as a sign of nobility or ...
, in their own carriage (usually Queen Alexandra's State Coach). The King's Bargemaster
The King's Bargemaster is a subordinate officer of the Royal Household of the Sovereign of the United Kingdom. Until the mid-19th century, the Royal Family frequently used a Royal barge for transport along the River Thames. The role of the King ...
and Watermen accompany it, acting as footmen (a reminder of past times when the regalia were brought from the Tower of London by river). On arrival at the Sovereign's Entrance, under the Victoria Tower
The Victoria Tower is a square tower at the south-west end of the Palace of Westminster in London, adjacent to Black Rod's Garden on the west and Old Palace Yard on the east. At , it is slightly taller than the Elizabeth Tower (formerly known ...
, the Crown is passed by the Bargemaster to the Comptroller of the Lord Chamberlain's Office
The Lord Chamberlain's Office is a department within the British Royal Household. It is concerned with matters such as protocol, state visits, investitures, garden parties, royal weddings and funerals. For example, in April 2005 it organised th ...
, under the watchful eye of the Crown Jeweller
The Crown Jeweller is responsible for the maintenance of the Crown Jewels of the United Kingdom, and is appointed by the British monarch. The current Crown Jeweller is Mark Appleby, who was appointed in 2017.
History
The post was created in 1843 ...
. The regalia are then carried to be displayed in the Royal Gallery
The Palace of Westminster serves as the meeting place for both the House of Commons and the House of Lords, the two houses of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. Informally known as the Houses of Parliament, the Palace lies on the north bank ...
. Also in the procession, usually in King Edward VII's Town Coach, are the two maces (separate from the three used by parliament) which are carried by the Serjeants-at-Arms of the Royal Household who escort the regalia in procession.
Arrival of the Sovereign and assembly of Parliament
 The monarch travels to the Palace of Westminster from Buckingham Palace in a state coach (since 2014, the
The monarch travels to the Palace of Westminster from Buckingham Palace in a state coach (since 2014, the Diamond Jubilee State Coach
The Diamond Jubilee State Coach (initially known as the State Coach Britannia) is an enclosed, six-horse-drawn carriage that was made to commemorate Queen Elizabeth II's 80th birthday, but completion was delayed for nearly eight years. Eventual ...
), arriving at the Sovereign's Entrance under the Victoria Tower
The Victoria Tower is a square tower at the south-west end of the Palace of Westminster in London, adjacent to Black Rod's Garden on the west and Old Palace Yard on the east. At , it is slightly taller than the Elizabeth Tower (formerly known ...
; the monarch is usually accompanied by his or her consort and sometimes by other members of the royal family. Senior members of the Royal Household follow in other carriages, and members of the armed forces line the processional route from Buckingham Palace to the Palace of Westminster. At the monarch's arrival, the national anthem is played, a gun salute
A gun salute or cannon salute is the use of a piece of artillery to fire shots, often 21 in number (''21-gun salute''), with the aim of marking an honor or celebrating a joyful event. It is a tradition in many countries around the world.
Histo ...
is sounded in Green Park
Green Park, officially The Green Park, is one of the Royal Parks of London. It is in the southern part – the core part – of the City of Westminster, Central London, but before that zone was extended to the north, to take in Marylebo ...
and the Royal Standard
In heraldry and vexillology, a heraldic flag is a flag containing coats of arms, heraldic badges, or other devices used for personal identification.
Heraldic flags include banners, standards, pennons and their variants, gonfalons, guidons, an ...
is hoisted in place of the Union Flag
The Union Jack, or Union Flag, is the ''de facto'' national flag of the United Kingdom. Although no law has been passed making the Union Flag the official national flag of the United Kingdom, it has effectively become such through precedent. ...
at the top of the Victoria Tower (where it remains until the monarch departs). The monarch is greeted on arrival by the Lord Great Chamberlain (who has oversight of the royal areas of the Palace of Westminster) and the Earl Marshal
Earl marshal (alternatively marschal or marischal) is a hereditary royal officeholder and chivalric title under the Monarchy of the United Kingdom, sovereign of the United Kingdom used in England (then, following the Act of Union 1800, in the U ...
(who has responsibility for State ceremonial), before proceeding to the Robing Room, where he or she puts on the Parliament Robe of State and the Imperial State Crown
The Imperial State Crown is one of the Crown Jewels of the United Kingdom and symbolises the sovereignty of the monarch.
It has existed in various forms since the 15th century. The current version was made in 1937 and is worn by the monarc ...
. A procession
A procession is an organized body of people walking in a formal or ceremonial manner.
History
Processions have in all peoples and at all times been a natural form of public celebration, as forming an orderly and impressive ceremony. Religious ...
is formed of heralds
A herald, or a herald of arms, is an officer of arms, ranking between pursuivant and king of arms. The title is commonly applied more broadly to all officers of arms.
Heralds were originally messengers sent by monarchs or noblemen to ...
, Great Officers of State
Government in medieval monarchies generally comprised the king's companions, later becoming the Royal Household, from which the officers of state arose, initially having household and government duties. Later some of these officers became ...
and members of the Royal Household, and when all is ready a fanfare is sounded and the monarch proceeds in State through the Royal Gallery to the House of Lords. Directly ahead of the monarch walk two peers: one (nowadays usually the Leader of the House of Lords
The leader of the House of Lords is a member of the Cabinet of the United Kingdom who is responsible for arranging government business in the House of Lords. The post is also the leader of the majority party in the House of Lords who acts as ...
) carrying the Cap of Maintenance
Typical of British heraldry, a cap of maintenance, known in heraldic language as a ''chapeau gules turned up ermine'', is a ceremonial cap of crimson velvet lined with ermine, which is worn or carried by certain persons as a sign of nobility or ...
, and the other (nowadays generally a retired senior military officer) carrying the Great Sword of State. Once seated on the throne, the monarch, wearing the Imperial State Crown, instructs the House by saying, "My Lords, pray be seated"; his or her consort takes their seat on the throne to the sovereign’s left and other members of the royal family may be seated elsewhere on the dais (for instance the Prince of Wales may be seated on a chair of state on a lower portion of the dais to the monarch's right).
Changes are sometimes made to suit the requirements of particular monarchs at particular times; for example in October 2019, the Queen attended in the usual ceremonial robes of state, but did not wear the Imperial State Crown; instead it was carried ahead of her in the procession and placed alongside the throne on a table.
Royal summons of the Commons to the Lords' chamber
 Motioned by the monarch, the Lord Great Chamberlain raises his white staff of office to signal the official known as Black Rod to summon the House of Commons. Black Rod turns and, under the escort of the Door-keeper of the House of Lords, proceeds to the Members' Lobby of the
Motioned by the monarch, the Lord Great Chamberlain raises his white staff of office to signal the official known as Black Rod to summon the House of Commons. Black Rod turns and, under the escort of the Door-keeper of the House of Lords, proceeds to the Members' Lobby of the House of Commons
The House of Commons is the name for the elected lower house of the bicameral parliaments of the United Kingdom and Canada. In both of these countries, the Commons holds much more legislative power than the nominally upper house of parliament. ...
, and reaches the doors of the Commons.
On Black Rod's approach, the Doorkeeper of the Commons orders that the doors are slammed shut against them, symbolising the rights of parliament and its independence from the monarch. The Usher of the Black Rod then strikes with the end of their ceremonial staff (the Black Rod) three times on the closed doors of the Commons Chamber, and is then admitted (there is a mark on the door of the Commons showing the repeated indentations made by Black Rods over the years.)
 This ritual is strongly associated with the occasion when (in 1642) King
This ritual is strongly associated with the occasion when (in 1642) King Charles I Charles I may refer to:
Kings and emperors
* Charlemagne (742–814), numbered Charles I in the lists of Holy Roman Emperors and French kings
* Charles I of Anjou (1226–1285), also king of Albania, Jerusalem, Naples and Sicily
* Charles I of ...
stormed into the House of Commons
The House of Commons is the name for the elected lower house of the bicameral parliaments of the United Kingdom and Canada. In both of these countries, the Commons holds much more legislative power than the nominally upper house of parliament. ...
in an unsuccessful attempt to arrest five Members of Parliament, including the celebrated English patriot and leading parliamentarian John Hampden
John Hampden (24 June 1643) was an English landowner and politician whose opposition to arbitrary taxes imposed by Charles I made him a national figure. An ally of Parliamentarian leader John Pym, and cousin to Oliver Cromwell, he was one of t ...
. (Since that time, no British monarch has entered the House of Commons when it is sitting.) The door-closing ritual, however, predates the 1640s, and although it has long since come to symbolise the independence of the Lower House, its primary purpose (according to Erskine May
Thomas Erskine May, 1st Baron Farnborough, (8 February 1815 – 17 May 1886) was a British constitutional theorist and Clerk of the House of Commons.
His seminal work, ''A Treatise upon the Law, Privileges, Proceedings and Usage of Parliame ...
) is for the Commons to establish Black Rod's identity. (Once this has been achieved, Black Rod cannot be refused admission, and all other business of whatever kind in the House must cease.)
The doors having been opened, the Chief Door-keeper of the House of Commons introduces Black Rod. At the bar, Black Rod bows to the Speaker before proceeding to the table, bowing again, and announcing the command of the monarch for the attendance of the Commons, in the following words:
A tradition developed in recent years for this command to be greeted with a defiant topical comment by republican-leaning Labour MP (until 2019) Dennis Skinner
Dennis Edward Skinner (born 11 February 1932) is a British former politician who served as Member of Parliament (MP) for Bolsover for 49 years, from 1970 to 2019. He is a member of the Labour Party.
Known for his left-wing views and acerbic w ...
, upon which, with some mirth, the House rises to make their way to the Lords' Chamber. This customary intervention was omitted by Mr Skinner in 2015, claiming that he had "bigger fish to fry than uttering something", due to a dispute over seating with the Scottish Nationalists. Skinner resumed the practice in 2016, until he was unseated in 2019.
Procession of the Commons
 The Speaker proceeds to attend the summons at once. The Serjeant-at-Arms picks up the ceremonial mace and, with the Speaker and Black Rod, leads the Members of the House of Commons as they walk, in pairs, towards the House of Lords. By custom, the members saunter, with much discussion and joking, rather than formally process. The
The Speaker proceeds to attend the summons at once. The Serjeant-at-Arms picks up the ceremonial mace and, with the Speaker and Black Rod, leads the Members of the House of Commons as they walk, in pairs, towards the House of Lords. By custom, the members saunter, with much discussion and joking, rather than formally process. The Prime Minister
A prime minister, premier or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. Under those systems, a prime minister i ...
and the Leader of the Opposition followed by The Deputy Prime Minister
A deputy prime minister or vice prime minister is, in some countries, a government minister who can take the position of acting prime minister when the prime minister is temporarily absent. The position is often likened to that of a vice president ...
, First Secretary of State
The First Secretary of State is an office that is sometimes held by a minister of the Crown in the Government of the United Kingdom. The office indicates seniority, including over all other Secretaries of State. The office is not always in use, ...
or another member of the government and the Deputy Leader of the Opposition usually walk side by side, leading the two lines of MPs. The Commons then arrive at the Bar of the House of Lords. The only people required to bow are the House of Commons Speaker, Commons Clerk, senior Lords official Black Rod and the Serjeant-at-Arms. No person who is not a member of the Upper House may pass the Bar unbidden when it is in session; a similar rule applies to the Commons. They remain standing at the Bar during the speech.
Delivery of the speech from the throne

 The monarch reads a prepared speech, known as the "
The monarch reads a prepared speech, known as the "Speech from the Throne
A speech from the throne, or throne speech, is an event in certain monarchies in which the reigning sovereign, or a representative thereof, reads a prepared speech to members of the nation's legislature when a session is opened, outlining th ...
" or the "Queen's/King's Speech", outlining the Government's agenda for the coming year. The speech is written by the Prime Minister and their cabinet members, and reflects the legislative agenda for which the Government seeks the agreement of both Houses of Parliament
The Palace of Westminster serves as the meeting place for both the House of Commons and the House of Lords, the two houses of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. Informally known as the Houses of Parliament, the Palace lies on the north ban ...
. It is traditionally written on goatskin vellum
Vellum is prepared animal skin or membrane, typically used as writing material. Parchment is another term for this material, from which vellum is sometimes distinguished, when it is made from calfskin, as opposed to that made from other anima ...
, and presented on bended knee for the monarch to read by the Lord Chancellor
The lord chancellor, formally the lord high chancellor of Great Britain, is the highest-ranking traditional minister among the Great Officers of State in Scotland and England in the United Kingdom, nominally outranking the prime minister. The ...
, who produces the scroll from a satchel-like bag. Traditionally, rather than turning their back on the Sovereign, which might appear disrespectful, the Lord Chancellor walks backwards down the steps of the throne, continuing to face the monarch. Lord Irvine of Lairg
Alexander Andrew Mackay Irvine, Baron Irvine of Lairg, (born 23 June 1940), known as Derry Irvine, is a Scottish lawyer, judge and political figure who served as Lord Chancellor under his former pupil barrister, Tony Blair.
Education
Irvine wa ...
, the Lord Chancellor at the time, sought to break the custom and applied successfully for permission to turn his back on the sovereign and walk down the steps forwards. The next Lord Chancellor, Jack Straw
John Whitaker Straw (born 3 August 1946) is a British politician who served in the Cabinet from 1997 to 2010 under the Labour governments of Tony Blair and Gordon Brown. He held two of the traditional Great Offices of State, as Home Secretary ...
, continued the former tradition but succeeding Lords Chancellor have chosen to walk forwards.
The whole speech is addressed to "My Lords and Members of the House of Commons", with one significant exception that the monarch says specifically, "Members of the House of Commons, estimates for the public services will be laid before you", since the budget is constitutionally reserved to the Commons.
The monarch reads the entire speech in a neutral and formal tone, implying neither approval nor disapproval of the proposals of their Government: the monarch makes constant reference to "My Government" when reading the text. After listing the main bills to be introduced during the session, the monarch states: "Other measures will be laid before you", thus leaving the government scope to introduce bills not mentioned in the speech. The monarch mentions any state visits they intend to make and also any planned state visits of foreign heads of state to the United Kingdom during the parliamentary session. The monarch concludes the speech in saying:
"My Lords and Members of the House of Commons, I pray that the blessing of Almighty God may rest upon your counsels".Traditionally, the members of both houses of Parliament listen to the speech respectfully, neither applauding nor showing dissent towards its contents before it is debated in each house. This silence, however, was broken in 1998, when Queen Elizabeth II announced the government's plan of abolishing the right of hereditary peers to automatically sit in the House of Lords. A few Labour members of the House of Commons cried "yes" and "hear", prompting several of the Lords to shout "no" and "shame". The Queen continued delivering her speech without any pause, ignoring the intervention. The conduct of those who interrupted the speech was strongly criticised at the time.
Departure of monarch

 Following the speech, the monarch and his or her retinue leave the chamber. The monarch bows to both sides of the House of Peers and then leaves the chamber, in the reverse order of the usual procession, before the Commons bow again and return to their Chamber.
Following the speech, the monarch and his or her retinue leave the chamber. The monarch bows to both sides of the House of Peers and then leaves the chamber, in the reverse order of the usual procession, before the Commons bow again and return to their Chamber.
Debate on the speech
After the departure of the King from the palace, each Chamber proceeds to the consideration of an "Address in Reply to His Majesty's Gracious Speech." But first, each House considers a bill ''pro forma
The term ''pro forma'' (Latin for "as a matter of form" or "for the sake of form") is most often used to describe a practice or document that is provided as a courtesy or satisfies minimum requirements, conforms to a norm or doctrine, tends to ...
'' to symbolise their right to deliberate independently of the monarch. In the House of Lords, the bill is called the Select Vestries Bill
A bill for the better regulating of Select Vestries, usually referred to as the Select Vestries Bill, is customarily the first bill introduced and debated in the United Kingdom's House of Lords at the start of each session of Parliament. The equiva ...
, while the Commons equivalent is the Outlawries Bill
A Bill for the more effectual preventing clandestine Outlawries, usually referred to as the Outlawries Bill, is customarily the first bill on the agenda of the United Kingdom's House of Commons at the start of each session of Parliament. It is us ...
. The bills are considered for the sake of ceremony only, and do not make any actual legislative progress. For the address in reply, a chosen member moves "That an humble Address be presented to His Majesty, as follows". The following is the form used in the House of Lords and is nearly identical to that used in the House of Commons:
The first speech of the debate in the Commons is, by tradition, a humorous one given by a member selected in advance. The consideration of the address in reply to the Throne Speech is the occasion for a debate on the Government's agenda. The debate on the Address in Reply is spread over several days. On each day, a different topic, such as foreign affairs or finance, is considered. The debate provides an indication of the views of Parliament regarding the government's agenda.
Following this debate, a vote is taken on the Government Programme. This vote is treated as a vote of no confidence
A motion of no confidence, also variously called a vote of no confidence, no-confidence motion, motion of confidence, or vote of confidence, is a statement or vote about whether a person in a position of responsibility like in government or mana ...
and losing this vote will automatically trigger a general election. When the Fixed-term Parliaments Act was in force, a general election was not automatically triggered if the vote was lost.
Variations
Openings in the absence of the monarch
Since 1901 the monarch has opened Parliament in person on all but seven occasions. In 1929 and 1935 King George V was too ill to attend; in 1951 King George VI was too ill to attend; in 1959 and 1963 Queen Elizabeth II was pregnant and did not attend. In each of these yearsLords Commissioners
The Lords Commissioners are privy counsellors appointed by the monarch of the United Kingdom to exercise, on his or her behalf, certain functions relating to Parliament which would otherwise require the monarch's attendance at the Palace of Wes ...
were appointed to preside over the opening, with the speech being read by the Presiding Commissioner (namely the Lord Chancellor). The speech was prefaced with the words:
"My Lords and Members of the House of Commons, We are commanded to deliver to you His/Her Majesty’s Speech in His/Her Majesty’s own words".In 2022, when the Queen was absent on the day due to 'episodic mobility problems', the heir-apparent to the throne and his elder son (the
Prince of Wales
Prince of Wales ( cy, Tywysog Cymru, ; la, Princeps Cambriae/Walliae) is a title traditionally given to the heir apparent to the English and later British throne. Prior to the conquest by Edward I in the 13th century, it was used by the rulers ...
and the Duke of Cambridge
Duke of Cambridge, one of several current royal dukedoms in the United Kingdom , is a hereditary title of specific rank of nobility in the British royal family. The title (named after the city of Cambridge in England) is heritable by male de ...
) were appointed to open Parliament as Counsellors of State
Counsellors of State are senior members of the British royal family to whom the monarch can delegate and revoke royal functions through letters patent under the Great Seal, to prevent delay or difficulty in the dispatch of public business in t ...
, with the Prince of Wales
Prince of Wales ( cy, Tywysog Cymru, ; la, Princeps Cambriae/Walliae) is a title traditionally given to the heir apparent to the English and later British throne. Prior to the conquest by Edward I in the 13th century, it was used by the rulers ...
reading the speech from the consort's throne on this occasion.
"Dressed down" State Openings
On certain occasions through history, some ceremonial aspects of the State Opening have been scaled back for specific reasons (including plague in 1593, threats of assassination in 1679, and war in 1939-1945). On three occasions in the reign of Queen Elizabeth II (in March 1974, June 2017 and December 2019), the State Opening has been conducted in a "dressed-down" manner, due to the snap general elections held in those years. On these occasions the Queen attended in day dress, rather than the traditional ceremonial robes of state; theImperial State Crown
The Imperial State Crown is one of the Crown Jewels of the United Kingdom and symbolises the sovereignty of the monarch.
It has existed in various forms since the 15th century. The current version was made in 1937 and is worn by the monarc ...
was carried in front of the Queen, rather than worn; inside the Palace, there were reduced numbers in the procession; and outside, motor cars were used in place of horse-drawn carriages, no military escort accompanied them. Otherwise, the ceremony remained largely the same.
In 2021, the ceremony was also scaled down due to the COVID-19 pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic, also known as the coronavirus pandemic, is an ongoing global pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The novel virus was first identif ...
. The Queen arrived by car at Westminster, and seating was restricted – 74 were allowed in the Lords Chamber, whilst 34 further MPs and peers were able to participate from the gallery. The Queen also attended in day dress. To prevent the spread of the virus, mask-wearing and testing was enforced, and the Lord Chancellor did not directly pass the speech to the Queen, but placed it on a table next to the throne.
The State Opening in May 2022 also took place with reduced ceremonial, due to the Queen suffering 'episodic mobility problems' (which eventually led to her being absent on the day).
Double and cancelled Openings
Throughout the twentieth century (including in wartime) the State Opening took place on an annual basis, with the following exceptions: * There were two State Openings in 1914 (and no State Opening in 1915); * There were two State Openings in 1921 (and no State Opening in 1923); * There were two State Openings in 1924 (and no State Opening in 1925); * There were two State Openings in 1974 In the twenty-first century the State Opening continued on an annual basis up to and including 2010, since when the following situations occurred: * There was no State Opening in 2011, as it was cancelled to ease the pressure for the planned introduction of legislation for fixed-term Parliaments; * There was no State Opening in 2018, as it was cancelled to lengthen the timeframe for the passing ofBrexit
Brexit (; a portmanteau of "British exit") was the withdrawal of the United Kingdom (UK) from the European Union (EU) at 23:00 GMT on 31 January 2020 (00:00 1 February 2020 CET).The UK also left the European Atomic Energy Community (EAEC or ...
-related legislation.
* There were two State Openings in 2019 (and no State Opening in 2020).
History
Origins
The Opening of Parliament began out of practical necessity. By the late 14th century, the manner in which the King gathered his nobles and representatives of the Commons had begun to follow an established pattern. First of all,Peers
Peers may refer to:
People
* Donald Peers
* Edgar Allison Peers, English academician
* Gavin Peers
* John Peers, Australian tennis player
* Kerry Peers
* Mark Peers
* Michael Peers
* Steve Peers
* Teddy Peers (1886–1935), Welsh international ...
' names were checked against the list of those who had been summoned, and representatives of the Commons were checked against the sheriffs' election returns. The Peers were robed and sat in the Painted Chamber
The Painted Chamber was part of the medieval Palace of Westminster. It was gutted by fire in 1834, and has been described as "perhaps the greatest artistic treasure lost in the fire". The room was re-roofed and re-furnished to be used tempora ...
at Westminster
Westminster is an area of Central London, part of the wider City of Westminster.
The area, which extends from the River Thames to Oxford Street, has many visitor attractions and historic landmarks, including the Palace of Westminster, Bu ...
; the Commons were summoned, and stood at the Bar (threshold) of the Chamber. A speech or sermon was then given (usually by the Lord Chancellor
The lord chancellor, formally the lord high chancellor of Great Britain, is the highest-ranking traditional minister among the Great Officers of State in Scotland and England in the United Kingdom, nominally outranking the prime minister. The ...
) explaining why Parliament had been summoned, after which the Lords and Commons went separately to discuss the business in hand. The monarch normally presided, not only for the Opening but also for the deliberations which followed (unless prevented by illness or other pressing matters).
The Tudors
In the Tudor period, the modern structure of Parliament began to emerge, and the monarch no longer attended during normal proceedings. For this reason, the State Opening took on greater symbolic significance as an occasion for the full constitution of the State (Monarch, Lords and Commons) to be seen. In this period, the parliamentary gathering began to be preceded by an open-air StateProcession
A procession is an organized body of people walking in a formal or ceremonial manner.
History
Processions have in all peoples and at all times been a natural form of public celebration, as forming an orderly and impressive ceremony. Religious ...
(which often attracted large numbers of onlookers): the Monarch, together with Household retinue, would proceed in State from whichever royal residence was being used, first to Westminster Abbey for a service (usually a Mass of the Holy Ghost, prior to the Reformation), and thence on foot (accompanied by the Lords Spiritual and Temporal in their robes) to the Palace of Westminster for the Opening itself.
 The Wriothesley Garter Book, a 1523 illustration by
The Wriothesley Garter Book, a 1523 illustration by Thomas Wriothesley
Sir Thomas Wriothesley ( ; died 24 November 1534) was a long serving officer of arms at the College of Arms in London. He was the son of Garter King of Arms, John Writhe, and he succeeded his father in this office.
Personal life
Wriothesley wa ...
, depicts King Henry VIII seated in Parliament in that year. It shows a remarkable visual similarity between State Openings of the 16th and 21st centuries. In both cases, the monarch sits on a throne
A throne is the seat of state of a potentate or dignitary, especially the seat occupied by a sovereign on state occasions; or the seat occupied by a pope or bishop on ceremonial occasions. "Throne" in an abstract sense can also refer to the mona ...
before the Cloth of Estate, crowned and wearing a crimson robe of state; at his right hand sit Cardinal Thomas Wolsey
Thomas Wolsey ( – 29 November 1530) was an English statesman and Catholic bishop. When Henry VIII became King of England in 1509, Wolsey became the king's Lord High Almoner, almoner. Wolsey's affairs prospered and by 1514 he had become the ...
, Archbishop of York
The archbishop of York is a senior bishop in the Church of England, second only to the archbishop of Canterbury. The archbishop is the diocesan bishop of the Diocese of York and the metropolitan bishop of the province of York, which covers th ...
and Lord Chancellor
The lord chancellor, formally the lord high chancellor of Great Britain, is the highest-ranking traditional minister among the Great Officers of State in Scotland and England in the United Kingdom, nominally outranking the prime minister. The ...
, with arms above under a cardinal's hat, and William Warham
William Warham ( – 22 August 1532) was the Archbishop of Canterbury from 1503 to his death.
Early life and education
Warham was the son of Robert Warham of Malshanger in Hampshire. He was educated at Winchester College and New College, Oxford ...
, Archbishop of Canterbury
The archbishop of Canterbury is the senior bishop and a principal leader of the Church of England, the ceremonial head of the worldwide Anglican Communion and the diocesan bishop of the Diocese of Canterbury. The current archbishop is Justi ...
, with arms above. Behind stands Cuthbert Tunstall
Cuthbert Tunstall (otherwise spelt Tunstal or Tonstall; 1474 – 18 November 1559) was an English Scholastic, church leader, diplomat, administrator and royal adviser. He served as Prince-Bishop of Durham during the reigns of Henry VIII, Edwar ...
, Bishop of London
A bishop is an ordained clergy member who is entrusted with a position of authority and oversight in a religious institution.
In Christianity, bishops are normally responsible for the governance of dioceses. The role or office of bishop is ca ...
.See catalogue entry, royal collection/ref> The
Cap of Maintenance
Typical of British heraldry, a cap of maintenance, known in heraldic language as a ''chapeau gules turned up ermine'', is a ceremonial cap of crimson velvet lined with ermine, which is worn or carried by certain persons as a sign of nobility or ...
and Sword of State are borne by peers standing before the monarch on the left and right respectively; the Lord Great Chamberlain stands alongside, bearing his white wand of office, near the Garter King of Arms in his tabard
A tabard is a type of short coat that was commonly worn by men during the late Middle Ages and early modern period in Europe. Generally worn outdoors, the coat was either sleeveless or had short sleeves or shoulder pieces. In its more develope ...
displaying the royal arms (Thomas Wriothesley himself, the illustrator). Members of the Royal retinue are arrayed behind the King (top right). In the main body of the Chamber, the Bishops are seated on benches to the King's right wearing their parliamentary robes, with the Mitred Abbots behind them. The Lords Temporal are seated to the King's left and on the cross-bench, the status of peers is indicated by the number of miniver bars (white fur edged with gold oak-leaf lace) on their peerage robes: 4 for a duke, 3½ for a marquess, 3 for an earl, 2½ for a viscount, and 2 for a baron. Thus there are 2 dukes, both wearing ducal coronets, the first holding a Marshal's Baton, thus he is the Duke of Norfolk
Duke of Norfolk is a title in the peerage of England. The seat of the Duke of Norfolk is Arundel Castle in Sussex, although the title refers to the county of Norfolk. The current duke is Edward Fitzalan-Howard, 18th Duke of Norfolk. The dukes ...
, Earl Marshal
Earl marshal (alternatively marschal or marischal) is a hereditary royal officeholder and chivalric title under the Monarchy of the United Kingdom, sovereign of the United Kingdom used in England (then, following the Act of Union 1800, in the U ...
of England. William Weston, Prior of the Hospital of St John of Jerusalem, premier baron in the roll of peers, dressed in black, sits at the end of the cross-bench. The judges (red-robed and coif
A coif () is a close fitting cap worn by both men and women that covers the top, back, and sides of the head.
History
Coifs date from the 10th century, but fell out of popularity with men in the 14th century."A New Look for Women." Arts and ...
ed) are on the woolsack
The Woolsack is the seat of the Lord Speaker in the House of Lords, the Upper House of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. Before 2006, it was the seat of the Lord Chancellor.
History
In the 14th century King Edward III (1327–1377) said th ...
s in the centre (two Chief Justices, eight judges, and four Serjeants-at-Law
A Serjeant-at-Law (SL), commonly known simply as a Serjeant, was a member of an order of barristers at the English and Irish Bar. The position of Serjeant-at-Law (''servientes ad legem''), or Sergeant-Counter, was centuries old; there are wri ...
), and behind them kneel the clerks (with quills and inkpots). At the bottom of the picture members of the House of Commons can be seen behind the Bar of the House, with Thomas More
Sir Thomas More (7 February 1478 – 6 July 1535), venerated in the Catholic Church as Saint Thomas More, was an English lawyer, judge, social philosopher, author, statesman, and noted Renaissance humanist. He also served Henry VIII as Lord ...
, Speaker of the House of Commons Speaker of the House of Commons is a political leadership position found in countries that have a House of Commons, where the membership of the body elects a speaker to lead its proceedings.
Systems that have such a position include:
* Speaker of ...
, in the centre, wearing his black and gold robe of state.
The Mitred Abbots were removed from Parliament at the time of the Reformation.
Subsequent developments
 Since that time the ceremonial has evolved, but not dramatically. In 1679 neither the procession nor the Abbey service took place, due to fears of a Popish Plot; although the procession was subsequently restored, the service in the Abbey was not. The monarch's role in the proceedings changed over time: early on, the monarch would say some introductory words, before calling upon the Lord Chancellor (or Lord Keeper) to address the assembly. James I, however, was accustomed to speak at greater length himself, and sometimes dispensed with the Chancellor's services as spokesman. This varying pattern continued in subsequent reigns (and during the Commonwealth, when Cromwell gave the speech), but from 1679 onwards it became the norm for the monarch alone to speak. Since then, the monarch (if present) has almost invariably given the speech, with the exception of George I (whose command of English was poor) and Victoria (after the death of Prince Albert). A dramatic change was occasioned by the destruction of the old Palace of Westminster by fire in 1834; however, the new palace was designed with the ceremony of the State Opening very much in mind, and the modern ceremony dates from its opening in 1852. The entire State Opening of Parliament was filmed and televised for the first time in 1958.
In 1998, adjustments were made to the ceremonial inside Parliament to shorten the proceedings. The
Since that time the ceremonial has evolved, but not dramatically. In 1679 neither the procession nor the Abbey service took place, due to fears of a Popish Plot; although the procession was subsequently restored, the service in the Abbey was not. The monarch's role in the proceedings changed over time: early on, the monarch would say some introductory words, before calling upon the Lord Chancellor (or Lord Keeper) to address the assembly. James I, however, was accustomed to speak at greater length himself, and sometimes dispensed with the Chancellor's services as spokesman. This varying pattern continued in subsequent reigns (and during the Commonwealth, when Cromwell gave the speech), but from 1679 onwards it became the norm for the monarch alone to speak. Since then, the monarch (if present) has almost invariably given the speech, with the exception of George I (whose command of English was poor) and Victoria (after the death of Prince Albert). A dramatic change was occasioned by the destruction of the old Palace of Westminster by fire in 1834; however, the new palace was designed with the ceremony of the State Opening very much in mind, and the modern ceremony dates from its opening in 1852. The entire State Opening of Parliament was filmed and televised for the first time in 1958.
In 1998, adjustments were made to the ceremonial inside Parliament to shorten the proceedings. The herald
A herald, or a herald of arms, is an officer of arms, ranking between pursuivant and king of arms. The title is commonly applied more broadly to all officers of arms.
Heralds were originally messengers sent by monarchs or noblemen to ...
s, instead of processing with the monarch, arrived at Parliament earlier and had a separate procession. The number of court officials in the procession was reduced, including one of the ladies in waiting
A lady-in-waiting or court lady is a female personal assistant at a court, attending on a royal woman or a high-ranking noblewoman. Historically, in Europe, a lady-in-waiting was often a noblewoman but of lower rank than the woman to whom sh ...
and the Crown Equerry. Also omitted were the three Heads of the Armed Services, represented instead by the Chief of the Defence Staff. Silver Stick in Waiting (the Commander of the Household Cavalry) no longer processed, although Gold Stick-in-Waiting (the honorary Colonel of the Household Cavalry) retained a place.
Equivalents in other countries
 Similar ceremonies are held in other
Similar ceremonies are held in other Commonwealth realm
A Commonwealth realm is a sovereign state in the Commonwealth of Nations whose monarch and head of state is shared among the other realms. Each realm functions as an independent state, equal with the other realms and nations of the Commonwealt ...
s. The governor-general or, in the case of Australia's states and Canada's provinces
Within the geographical areas of Canada, the ten provinces and three territories are sub-national administrative divisions under the jurisdiction of the Canadian Constitution. In the 1867 Canadian Confederation, three provinces of British North ...
, the relevant governor
A governor is an administrative leader and head of a polity or political region, ranking under the head of state and in some cases, such as governors-general, as the head of state's official representative. Depending on the type of political ...
or lieutenant governor, respectively, usually delivers the speech from the throne. On occasion, the monarch may open these parliaments and deliver the speech herself. In both Australia and Canada, the last time this occurred was in 1977. In New Zealand, the monarch last opened parliament personally in February 1990.
In India, the President of India
The president of India ( IAST: ) is the head of state of the Republic of India. The president is the nominal head of the executive, the first citizen of the country, as well as the commander-in-chief of the Indian Armed Forces. Droupadi Murmu ...
opens Parliament with an address similar to the Speech from the Throne. This is also the case in Commonwealth Republics with a non-executive Presidency such as Malta
Malta ( , , ), officially the Republic of Malta ( mt, Repubblika ta' Malta ), is an island country in the Mediterranean Sea. It consists of an archipelago, between Italy and Libya, and is often considered a part of Southern Europe. It lies ...
, Mauritius
Mauritius ( ; french: Maurice, link=no ; mfe, label=Mauritian Creole, Moris ), officially the Republic of Mauritius, is an island nation in the Indian Ocean about off the southeast coast of the African continent, east of Madagascar. It incl ...
and Singapore
Singapore (), officially the Republic of Singapore, is a sovereign island country and city-state in maritime Southeast Asia. It lies about one degree of latitude () north of the equator, off the southern tip of the Malay Peninsula, borde ...
.
 In the
In the Netherlands
)
, anthem = ( en, "William of Nassau")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of the Netherlands
, established_title = Before independence
, established_date = Spanish Netherl ...
a similar ceremony is held on the third Tuesday in September, which is called ''Prinsjesdag
Prinsjesdag ( en, Little Prince's Day) is the day on which the reigning Monarchy of the Netherlands, monarch of the Netherlands addresses a joint session of the States General of the Netherlands, States-General of the Netherlands (consisting o ...
'' in the Netherlands. Article 65 of the constitution states that "A statement of the policy to be pursued by the Government is given by or on behalf of the King before a joint session of the two Houses of the States General that is held every year on the third Tuesday in September or on such earlier date as may be prescribed by Act of Parliament." In Norway, the King is required by Article 74 of the constitution to preside over the opening of the Storting after it had been declared to be legally constituted by the president of the Storting. After he delivers the Speech from the Throne, outlining the government's policies for the coming year, a member of the government reads the Report on the State of the Realm, an account of the government's achievements of the past year.
In Sweden a similar ceremony as the British was held until 1974, when the constitution was changed. The old opening of state was in Sweden called ''Riksdagens högtidliga öppnande'' ("The solemn opening of the Riksdag") and was, as the British, full of symbolism. After the abolition of the old state opening, the opening is now held in the Riksdag but in the presence of the monarch
A monarch is a head of stateWebster's II New College DictionarMonarch Houghton Mifflin. Boston. 2001. p. 707. Life tenure, for life or until abdication, and therefore the head of state of a monarchy. A monarch may exercise the highest authority ...
and his family. It is still the King who officially opens the parliament. After the opening of parliament the King gives a speech followed by the Prime Minister's declaration of government.
In Israel, a semi-annual ceremony, attended by the President
President most commonly refers to:
*President (corporate title)
* President (education), a leader of a college or university
* President (government title)
President may also refer to:
Automobiles
* Nissan President, a 1966–2010 Japanese ...
, opens the winter and summer sessions of the Knesset
The Knesset ( he, הַכְּנֶסֶת ; "gathering" or "assembly") is the unicameral legislature of Israel. As the supreme state body, the Knesset is sovereign and thus has complete control of the entirety of the Israeli government (with ...
. Though in the past he was a guest sitting in the Knesset's upper deck, the President now attends the ceremony from the speaker's podium and gives his own written address regarding the upcoming session. In the first session of each legislative period of the Knesset, the President has the duty of opening the first session himself and inaugurating the temporary Knesset speaker, and then conducting the inauguration process of all of the Knesset members.
In some countries with presidential or similar systems in which the roles of head of state
A head of state (or chief of state) is the public persona who officially embodies a state Foakes, pp. 110–11 " he head of statebeing an embodiment of the State itself or representatitve of its international persona." in its unity and l ...
and head of government are merged, the chief executive's annual speech to the legislative branch is imbued with some of the ceremonial weight of a parliamentary state opening. The most well-known example is the State of the Union Address
The State of the Union Address (sometimes abbreviated to SOTU) is an annual message delivered by the president of the United States to a joint session of the United States Congress near the beginning of each calendar year on the current conditi ...
in the United States. Other examples include the State of the Nation Address in the Philippines, a former American dependency. These speeches differ from a State Opening in at least two respects, however: they do not in fact open the legislative session, and they are delivered by the chief executive on his or her own behalf. In Poland, the President of Poland
The president of Poland ( pl, Prezydent RP), officially the president of the Republic of Poland ( pl, Prezydent Rzeczypospolitej Polskiej), is the head of state of Poland. Their rights and obligations are determined in the Constitution of Pola ...
delivers his speech to the ''Sejm
The Sejm (English: , Polish: ), officially known as the Sejm of the Republic of Poland (Polish: ''Sejm Rzeczypospolitej Polskiej''), is the lower house of the bicameral parliament of Poland.
The Sejm has been the highest governing body of t ...
'' and the Senate at the First Sitting of these Houses, which is similar to Speech from the Throne. It is rather a custom than a law. Most Presidents of Poland
The president of Poland ( pl, Prezydent RP), officially the president of the Republic of Poland ( pl, Prezydent Rzeczypospolitej Polskiej), is the head of state
A head of state (or chief of state) is the public persona who officiall ...
delivered the Speech to the Parliament
In modern politics, and history, a parliament is a legislative body of government. Generally, a modern parliament has three functions: representing the electorate, making laws, and overseeing the government via hearings and inquiries. Th ...
. The exception was in 2007, when President Lech Kaczyński
Lech Aleksander Kaczyński (; 18 June 194910 April 2010) was a Polish politician who served as the city mayor of Warsaw from 2002 until 2005, and as President of Poland from 2005 until his death in 2010. Before his tenure as president, he pre ...
, instead of addressing the ''Sejm'', watched the First Sitting of the 6th term ''Sejm'' from the Presidential box in the Press gallery. The President of Mexico
The president of Mexico ( es, link=no, Presidente de México), officially the president of the United Mexican States ( es, link=no, Presidente de los Estados Unidos Mexicanos), is the head of state and head of government of Mexico. Under the Co ...
used to be constitutionally obliged to deliver a speech, similar to the American State of the Union, until 2006 when President Vicente Fox
Vicente Fox Quesada (; born 2 July 1942) is a Mexican businessman and politician who served as the 62nd president of Mexico from 1 December 2000 to 30 November 2006. After campaigning as a right-wing populist, Fox was elected president on the ...
was impeded by the opposition parties from entering the Congress building for his sixth and final speech. Since that incident, the Constitution no longer requires the President's presence at the opening of Congress.
References
External links
Videos of every State Opening since 1988
at
C-SPAN
Cable-Satellite Public Affairs Network (C-SPAN ) is an American cable and satellite television network that was created in 1979 by the cable television industry as a nonprofit public service. It televises many proceedings of the United States ...
House of Lords FAQ: State Opening
at UK Parliament website
Parliamentary occasions: State Opening
at UK Parliament website
at
Hansard
''Hansard'' is the traditional name of the transcripts of parliamentary debates in Britain and many Commonwealth countries. It is named after Thomas Curson Hansard (1776–1833), a London printer and publisher, who was the first official print ...
Photos of the 2015 ceremony
at
Flickr
Flickr ( ; ) is an American image hosting and video hosting service, as well as an online community, founded in Canada and headquartered in the United States. It was created by Ludicorp in 2004 and was a popular way for amateur and profession ...
Newsreel footage
Newsreel of the 1958 ceremony
(the first time the ceremony was filmed)
Newsreel of the 1960 ceremony
(filmed for the first time in colour)
Newsreel of the 1966 ceremony
(the first time cameras were allowed in the House of Commons)
Newsreel of the 1970 ceremony
Newsreel of the November 1974 ceremony
(the second State Opening of that year) {{DEFAULTSORT:State Opening of Parliament Speeches by heads of state Parliament of the United Kingdom Opening ceremonies Ceremonies in the United Kingdom